human cell.ppt
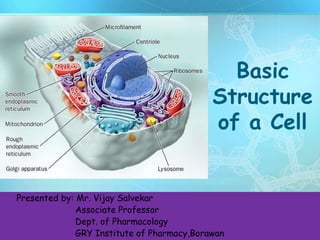
- 1. 1 Basic Structure of a Cell Presented by: Mr. Vijay Salvekar Associate Professor Dept. of Pharmacology GRY Institute of Pharmacy,Borawan
- 2. 2 History of Cells & the Cell Theory Virchow Cell Specialization
- 3. 3 First to View Cells • In 1665, Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork (dead plant cells) • What he saw looked like small boxes
- 4. 4 First to View Cells • Hooke is responsible for naming cells • Hooke called them “CELLS” because they looked like the small rooms that monks lived in called Cells
- 5. 5 Anton van Leeuwenhoek • In 1673, Leeuwenhoek (a Dutch microscope maker), was first to view organism (living things) • Leeuwenhoek used a simple, handheld microscope to view pond water & scrapings from his teeth
- 6. 6 Beginning of the Cell Theory • In 1838, a German botanist named Matthias Schleiden concluded that all plants were made of cells • Schleiden is a cofounder of the cell theory
- 7. 7 Beginning of the Cell Theory • In 1839, a German zoologist named Theodore Schwann concluded that all animals were made of cells • Schwann also cofounded the cell theory
- 8. 8 Beginning of the Cell Theory • In 1855, a German medical doctor named Rudolph Virchow observed, under the microscope, cells dividing • He reasoned that all cells come from other pre-existing cells by cell division
- 9. 9 CELL THEORY • All living things are made of cells • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) • Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
- 12. 12 Prokaryotes – The first Cells • Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles • Includes bacteria • Simplest type of cell • Single, circular chromosome
- 13. 13 Prokaryotes • Nucleoid region (center) contains the DNA • Surrounded by cell membrane & cell wall (peptidoglycan) • Contain ribosomes (no membrane) in their cytoplasm to make proteins
- 14. 14 Eukaryotes • Cells that HAVE a nucleus and membrane- bound organelles • Includes protists, fungi, plants, and animals • More complex type of cells
- 15. 15 Eukaryotic Cell Contain 3 basic cell structures: • Nucleus • Cell Membrane • Cytoplasm with organelles
- 16. 16 Two Main Types of Eukaryotic Cells Plant Cell Animal Cell
- 17. 17 Organelles
- 18. 18 Organelles • Very small (Microscopic) • Perform various functions for a cell • Found in the cytoplasm • May or may not be membrane- bound
- 19. 19 Cell or Plasma Membrane Outside of cell Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Cell membrane Proteins Protein channel Lipid bilayer Carbohydrate chains • Composed of double layer of phospholipids and proteins • Surrounds outside of ALL cells • Controls what enters or leaves the cell • Living layer
- 20. 20 Phospholipids • Heads contain glycerol & phosphate and are hydrophilic (attract water) • Tails are made of fatty acids and are hydrophobic (repel water) • Make up a bilayer where tails point inward toward each other • Can move laterally to allow small molecules (O2, CO2, & H2O to enter)
- 21. 21 The Cell Membrane is Fluid Molecules in cell membranes are constantly moving and changing
- 22. 22 Cell Membrane Proteins • Proteins help move large molecules or aid in cell recognition • Peripheral proteins are attached on the surface (inner or outer) • Integral proteins are embedded completely through the membrane
- 23. 23 • Lies immediately against the cell wall in plant cells • Pushes out against the cell wall to maintain cell shape Cell Membrane in Plants Cell membrane
- 24. 24 • Found outside of the cell membrane • Nonliving layer • Supports and protects cell • Found in plants, fungi, & bacteria Cell wall Cell Wall
- 25. 25 • Jelly-like substance enclosed by cell membrane • Provides a medium for chemical reactions to take place Cytoplasm of a Cell cytoplasm
- 26. 26 • Contains organelles to carry out specific jobs More on Cytoplasm cytoplasm
- 27. 27 • Controls the normal activities of the cell • Contains the DNA in chromosomes • Bounded by a nuclear envelope (membrane) with pores • Usually the largest organelle The Control Organelle - Nucleus
- 28. 28 • Each cell has fixed number of chromosomes that carry genes • Genes control cell characteristics Nucleus More on the Nucleus
- 29. 29 Nuclear Envelope • Double membrane surrounding nucleus • Also called nuclear membrane • Contains nuclear pores for materials to enter & leave nucleus Nuclear pores
- 30. 30 Inside the Nucleus - The genetic material (DNA) is found DNA is spread out And appears as CHROMATIN in non-dividing cells DNA is condensed & wrapped around proteins forming as CHROMOSOMES in dividing cells
- 31. 31 What Does DNA do? DNA is the hereditary material of the cell Genes that make up the DNA molecule code for different proteins
- 32. 32 Nucleolus • Inside nucleus • Disappears when cell divides • Makes ribosomes that make proteins
- 33. 33 Cytoskeleton • Helps cell maintain cell shape • Also help move organelles around • Made of proteins • Microfilaments are threadlike & made of ACTIN • Microtubules are tubelike & made of TUBULIN
- 35. 35 Centrioles • Found only in animal cells • Paired structures near nucleus • Made of bundle of microtubules • Appear during cell division forming mitotic spindle • Help to pull chromosome pairs apart to opposite ends of the cell
- 36. 36 Mitochondrion (plural = mitochondria) • “Powerhouse” of the cell • Generate cellular energy (ATP) • More active cells like muscle cells have MORE mitochondria • Both plants & animal cells have mitochondria • Site of CELLULAR RESPIRATION (burning glucose)
- 37. 37 MITOCHONDRIA Surrounded by a DOUBLE membrane Folded inner membrane called CRISTAE (increases surface area for more chemical Reactions) Has its own DNA Interior called MATRIX
- 38. 38 Interesting Fact --- • Mitochondria Come from cytoplasm in the EGG cell during fertilization Therefore … • You inherit your mitochondria from your mother!
- 39. 39 Endoplasmic Reticulum - ER Two kinds of ER ---ROUGH & SMOOTH • Network of hollow membrane tubules • Connects to nuclear envelope & cell membrane • Functions in Synthesis of cell products & Transport
- 40. 40 Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) • Has ribosomes on its surface • Makes membrane proteins and proteins for export out of cell
- 41. 41 Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) • Proteins are made by ribosomes on ER surface • They are then threaded into the interior of the Rough ER to be modified and transported
- 42. 42 Functions of the Smooth ER • Makes membrane lipids (steroids) • Regulates calcium (muscle cells) • Destroys toxic substances (Liver)
- 43. 43 Endomembrane System Includes nuclear membrane connected to ER connected to cell membrane (transport)
- 44. 44 Ribosomes • Made of PROTEINS and rRNA • “Protein factories” for cell • Join amino acids to make proteins through protein synthesis
- 45. 45 Ribosomes Can be attached to Rough ER OR Be free (unattached) in the cytoplasm
- 46. 46 Golgi Bodies • Stacks of flattened sacs • Have a shipping side (cis face) & a receiving side (trans face) • Receive proteins made by ER • Transport vesicles with modified proteins pinch off the ends Transport vesicle CIS TRANS
- 47. 47 Golgi Bodies Look like a stack of pancakes Modify, sort, & package molecules from ER for storage OR transport out of cell
- 48. 48 Golgi Animation Materials are transported from Rough ER to Golgi to the cell membrane by VESICLES
- 49. 49 Lysosomes • Contain digestive enzymes • Break down food, bacteria, and worn out cell parts for cells • Programmed for cell death (APOPTOSIS) • Lyse & release enzymes to break down & recycle cell parts)
- 50. 50 Lysosome Digestion • Cells take in food by phagocytosis • Lysosomes digest the food & get rid of wastes
- 51. 51 Cilia & Flagella • Function in moving cells, in moving fluids, or in small particles across the cell surface
- 52. 52 Cilia & Flagella • Cilia are shorter and more numerous on cells • Flagella are longer and fewer (usually 1-3) on cells
- 53. 53 Cell Movement with Cilia & Flagella
- 54. 54 Cilia Moving Away Dust Particles from the Lungs
- 55. 55 Vacuoles • Fluid filled sacks for storage • Small or absent in animal cells • Plant cells have a large Central Vacuole
- 56. 56 Vacuoles • In plants, they store Cell Sap • Includes storage of sugars, proteins, minerals, lipids, wastes, salts, water, and enzymes
